Probiotics are live, helpful microorganisms that are added to brackish water aquaculture environments to enhance the general health, growth, and welfare of aquatic animals such as shrimp and fish. These probiotics include yeasts such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and bacteria such as Bacillus spp., Nitrosomonas, and Nitrobacter that have been selected primarily because of their advantages in the specific conditions of brackish water, which contains salt concentrations that are intermediate between those of freshwater and seawater. By producing digestive enzymes, decomposing organic waste, along with taking part in vital processes like nitrification—which reduces detrimental ammonia and nitrite levels—they achieve the desired consequences.
Probiotics reduce the risk of disease by colonizing the gut, boosting nutrient absorption, strengthening immune responses, and outcompeting harmful microbes. They can be injected into meals, added to water, or supplied through bioencapsulation. Effective probiotic use contributes to healthier water quality, higher growth rates, increased resistance to disease, and increased resilience to environmental challenges.
On the other hand, a successful application necessitates adherence to regulatory requirements, careful strain selection of probiotics, proper dosage, and environmental condition control.
Benefits of Probiotics
They can help improve digestion, boost the immune system, and maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. Probiotics can also aid in the absorption of nutrients, reduce inflammation, and even support mental health by influencing the gut-brain axis. Consuming probiotics through foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and supplements can help promote overall well-being. Some benefits of probiotics are given below:
Improved Water Quality
Ammonia and Nitrite Reduction:
Probiotics that break down dangerous ammonia into nitrite and ultimately less hazardous nitrate, such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter, are essential to the nitrification process. Through this process, the water’s toxicity is decreased, making the habitat friendlier for aquatic life.
Organic Matter Degradation:
Enzymes produced by Bacillus species decompose organic waste, lowering waste accumulation and avoiding the accumulation of dangerous materials. The health of the aquatic species depends on the water becoming clearer and cleaner as a result of this.
Disease Prevention and Control
Competitive Exclusion:
Probiotics lower the risk of infections by competing with pathogenic bacteria for resources and attachment sites in the stomach and surrounding tissues. This process is called competitive exclusion. By occupying these spaces, probiotics prevent harmful bacteria from proliferating and spreading.
Antimicrobial Production:
Some probiotics have the capacity to produce antibiotic substances that directly prevent the spread of diseases. This natural approach to disease management promotes more sustainable and ecologically friendly aquaculture methods by reducing the need for drugs.
Immune system enhancement:
Probiotics can strengthen the immune systems of aquatic animals, making them more resilient to disease and reducing mortality rates.
Stress Reduction
Environmental Stability:
By continuously breaking down trash and lowering harmful metabolites, probiotics aid in the maintenance of steady water quality parameters. Environmental stability helps aquatic creatures avoid stress, which can otherwise result in health Problems and stunted growth.
Enhanced Resilience:
Probiotics increase an aquatic species’ resistance to environmental stressors such temperature swings, salinity variations, and handling stress by enhancing immune system performance and general health.
Enhanced Growth and Feed Efficiency
Production of Digestive Enzymes:
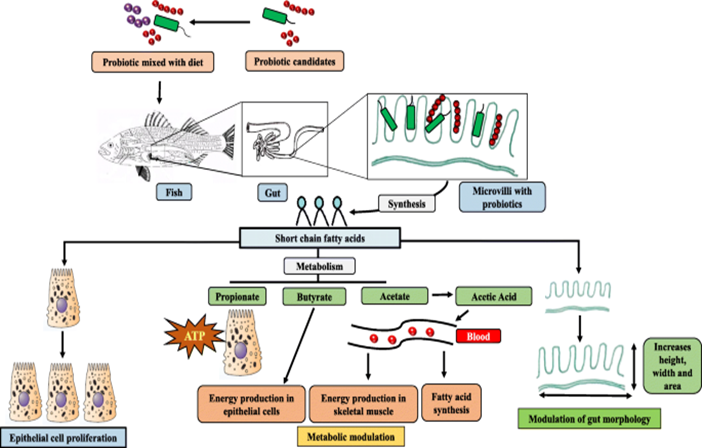
Probiotics aid in a more efficient decomposition of food components by producing a variety of digestive enzymes, including lipases, amylases, and proteases. This boosts growth rates and feed conversion ratios by increasing nutrient uptake and usage.
Improvement of Gut Health:
By improving the gut microbiota, probiotics such as Lactobacillus species support a healthy digestive tract. higher digestion and nutrition absorption from a healthier gut lead to higher growth and general health.
Stress Reduction
Environmental Stability:
Probiotics help to maintain stable water quality parameters by continuously breaking down trash and reducing toxic metabolites. Regular environmental conditions reduce stress on aquatic life, hence averting illnesses and stunted growth.
Enhanced Resilience:
By enhancing general health and immune function, probiotics assist aquatic organisms in getting more susceptible to environmental stresses such temperature fluctuations, salinity changes, and managing stress.
Sustainable Aquaculture Practices
Decreased Chemical Use:
Probiotic use can lessen the need for chemical treatments and antibiotics, which can harm the environment and breed resistant forms of bacteria.
Eco-Friendly Solution:
Probiotics offer an organic and sustainable approach to managing aquaculture systems, enhancing the sector’s long-term sustainability and safeguarding the surrounding ecosystems.
Enhanced Reproductive Performance
Broodstock Health:
Probiotics help broodstock remain healthier overall, which enhances their ability to reproduce and produces higher-quality offspring. Aquaculture operations are guaranteed to be sustainable since healthy broodstock have a higher probability of producing viable eggs and larvae.
Applications of Probiotics
Better Digestion
Feed containing probiotics aids in the production of digestive enzymes that facilitate the digestion of feed ingredients, enhancing feed conversion ratios and nutrient absorption.
Growth Promotion:
Probiotics help aquatic species grow more quickly and maintain better general health by enhancing digestion and nutrient absorption.
Mental Health:
Probiotics play a role in the gut-brain axis, influencing mood and mental health. They may help reduce symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress.
Skin Health:
Probiotics can improve skin conditions like eczema and acne by balancing the gut microbiome, which in turn can have a positive impact on skin health.
Oral Health:
Probiotics can contribute to oral health by reducing bad breath, preventing cavities, and promoting healthy gums.
Immune System Support:
Probiotics can enhance the immune system by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which helps in fighting off harmful pathogens.
Digestive Health:
Probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, aid in digestion, and alleviate issues like diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD).
Application Methods
There are 3 application methods of probiotics in brackish water aquaculture.
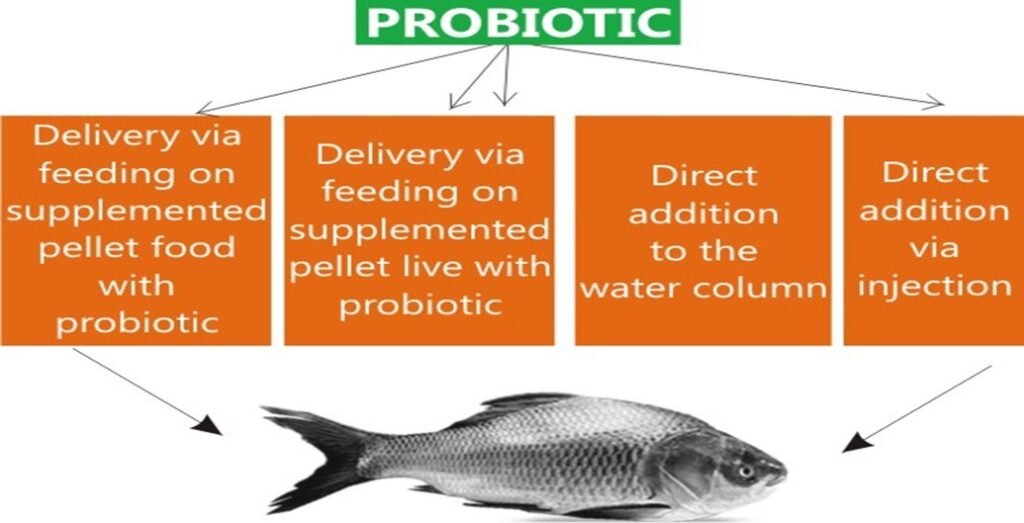
Direct Addition to Water
- Method: Probiotics are added directly to the aquaculture water to improve the microbial balance and water quality.
- Benefit: This method helps in the immediate improvement of water parameters by reducing harmful substances and enhancing beneficial microbial activity.
Incorporation into Feed
- Method: Probiotics are mixed with the feed or coated onto pellets, ensuring direct ingestion by the aquatic species.
- Benefit: This promotes gut health, improves digestion, and enhances nutrient absorption, directly benefiting the growth and health of the cultured species.
Bio-Encapsulation
- Method: Probiotics are encapsulated in live feed organisms such as Artemia (brine shrimp), which are then fed to the target species.
- Benefit: Ensures effective delivery and consumption of probiotics, particularly beneficial for early life stages of fish and shrimp.
