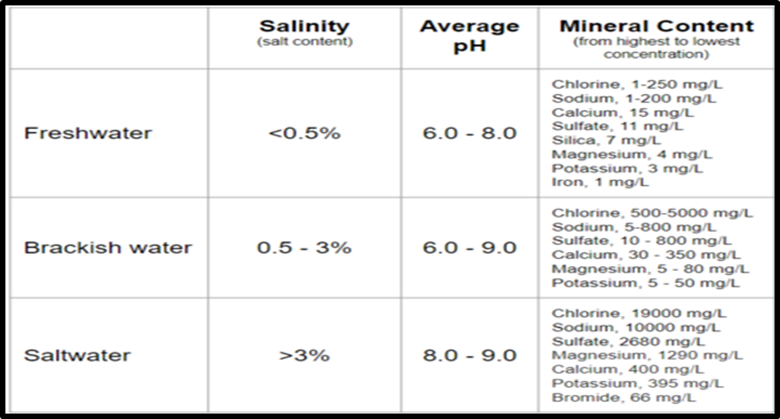
Water generally can be classified into three categories that is Fresh water, Brackish Water and Marine water. Fresh water is defined as the Water Which is enclosed by the earth crust and Salinity is less then 0.5 ppt and Marine water is that Water which encloses the earth crust and salinity is more then 35ppt. While Brackish water is piquant and briny than fresh water but not as salty as marine water. Brackish water has a wide range of salinity that is 0.5 to 30ppt.It can be created by combining fresh and salt water, as in estuaries, as well as by some human activities, most notably the construction of coastal marshland. Brackish water has a salty, disagreeable taste and a higher salinity (500–17,000 mg/l) than fresh water. But it is not as salty as marine water (30,000–40,000 mg/l). Water is classified primarily based on its salinity level, TDS, and conductivity. Conductivity, TDS, salinity of fresh water and marine water is 150-500 µs/cm, 1000 mg/l, 500 mg/l and 46,000-72,000 µs/cm, 30,000-40,000 mg/l, 35,000-40,000 mg/l respectively. Conductivity, TDS, and salinity of brackish water is 1000-46,000 µs/cm, 1000-5000 mg/l, and 500-17,000 mg/l respectively.
Brackish water habitats are dynamic. The salinity is influenced by the amount of freshwater that enters from rivers or rain, the tide, and evaporation rate. As a result, many fish species in brackish water environments can tolerate fluctuations in salinity. Brackish water is another significant source of aquatic life. Due to the tidal regime, brackish water is naturally present in estuaries, river deltas, lagoons in all over the world. Depending on the tide phase and the amount of fresh water discharged into the sea through the river, the salinity of the water in such ecosystems fluctuates dramatically, ranging from zero to 35 ppt. According to theory, brackish water has a specific gravity of 1.005 to 1.010 and contains between 0.5 and 30 grammes of salt per liter, which is more commonly expressed as 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand of salt. As a result, brackish water is a broad term that refers to a variety of salinity regimes. Estuaries, lakes, man-made pools, streams, aquifers, and underground water in different countries of the world are all places where brackish water can be found. Man-made sources of brackish water include dikes, which are walls constructed to restrict the flow of water from rivers and oceans, and the pools and streams that arise from purposefully flooding marshes for prawn farming. Lastly, deep fossil aquifers underground contain brackish groundwater. Because of ancient oceans, saltwater intrusion in coastal locations, or excessive mineral absorption when water percolates into the earth, groundwater can become brackish.

LOCATION OF BRACKISH WATER IN THE WORLD
| Salinity (PPT) | Name | Type | Countries | Reference |
| 3.40–3.60 | World Ocean | Ocean | Worldwide | Pérez and Chebude (2017) |
| 1.00-1.20 | Sea of Azov | Mediterranean Sea | Ukraine, Russia | Guinness world record |
| 1.14 | Sarygamysh Lake | Salt Lake | Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan | Aladin and Plotnikov (2004) |
| 35.0 | Garabogazköl | Lagoon | Turkmenistan | Hammer, U.T. (1986) |
| 32.4 | Lake Tuz (Tuz Gölü) | Salt Lake | Turkey | Almardini et al. (2015) |
| 2.30 | Lake Van | Salt Lake | Turkey | Susan et al 2018 |
| 3.00–4.00 | Lake Natron | Salt Lake | Tanzania | UNESCO |
| 3.80 | Mediterranean Sea | Mediterranean Sea | Southern Europe, Levant, North Africa | White et al. (2014) |
| 40.0 | Lake Retba | Salt Lake | Senegal | Russian Nature Reserved |
| 9.50 | Lake Techirghiol | Salt Lake | Romania | Lacu Sarat |
| 3.40 | Lough Hyne | Marine lake | Republic of Ireland | Observation on Lacu Sarat |
| 0.8 1.0 | Baltic Sea | Marginal sea | Northern Europe | Encyclopedia Britannica Online |
| 2.80–3.20 | Beaufort Sea | Marginal sea | North of Alaska and Canada | The Canadian Encyclopedia |
| 0.59 | Issyk Kul | Salt Lake | Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia | Dotsika et al. (2004) |
| 33.7 | Dead Sea | Salt Lake | Israel, Jordan, West Bank | Schutte et al. (2020) |
| 8.50–28.0 | Lake Urmia | Salt Lake | Iran | South-central Oregon |
| 3.17 | Chilika Lake | Lagoon | India | Lacul Techirghiol |
| 15.3 | Lake Pikrolimni | Salt Lake | Greece | Willever (2016) |
| 31.7 | Great Salt Lake, North Arm | Salt Lake | Great Basin, Utah, United States | Suosaari et al. (2016) |
| 14.2 | Great Salt Lake, South Arm | Salt Lake | Great Basin, Utah, United States | The Salton Sea Authority |
| 12.0 | Lake Abert | Salt Lake | Great Basin, Oregon, United States | El-Serehy et al. (2018) |
| 8.80 | Mono Lake | Salt Lake | Great Basin, California, United States | Science Learning Hub |
| 4.40 | Salton Sea | Salt Lake | Great Basin, California, United States | Anati (1999) |
| 43.3 | Gaet’ale Pond | Salt Lake | Ethiopia | Aquatic Resource Management |
| 3.60–4.10 | Red Sea | Mediterranean Sea | Egypt, Sudan, Arabian Peninsula, Horn of Africa | Ocean Salinity |
| 4.10–4.50 | Great Bitter Lake | Salt Lake | Egypt | Floods of Lake Eyre |
| 1.25 | Caspian Sea | Salt Lake | Eastern Europe/ Western Asia | Marine Nature Reserved |
| 34.8 | Lake Assal | Salt Lake | Djibouti | Horn of Africa |
| 1.40 | Qinghai Lake | Salt Lake | China | Republic of China |
| 18.0 | Little Manitou Lake | Salt Lake | Canada | Canadian Reserved Centre |
| 30.0 | Lake Sarat | Salt Lake | Braila, Romania | Facts about Romania |
| 2.20 | Sea of Marmara | Mediterranean Sea | Between the Balkan Peninsula and the Anatolian peninsula | Sea of Marmara |
| 1.30–2.30 | Black Sea | Mediterranean Sea | Between Europe and Asia – Balkan Peninsula, Eastern Europe, Anatolia, Caucasus | Sea of Marmara |
| 6.60 | Hamelin Pool | Lagoon | Australia | Indian Journal of Marine Sciences |
| 3.50+ | Lake Eyre | Endorheic lake | Australia | Indian Journal of Marine Sciences |
| 30.0 | Lake Baskunchak | Salt Lake | Astrakhan Oblast, Russia | The Black Sea Environment |
| 33.8 | Don Juan Pond | Salt Lake | Antarctica | National Oceanographic Centre |
| 0.00-14.6 | Lake Vanda | meromictic lake | Antarctica | National Oceanographic Centre |
